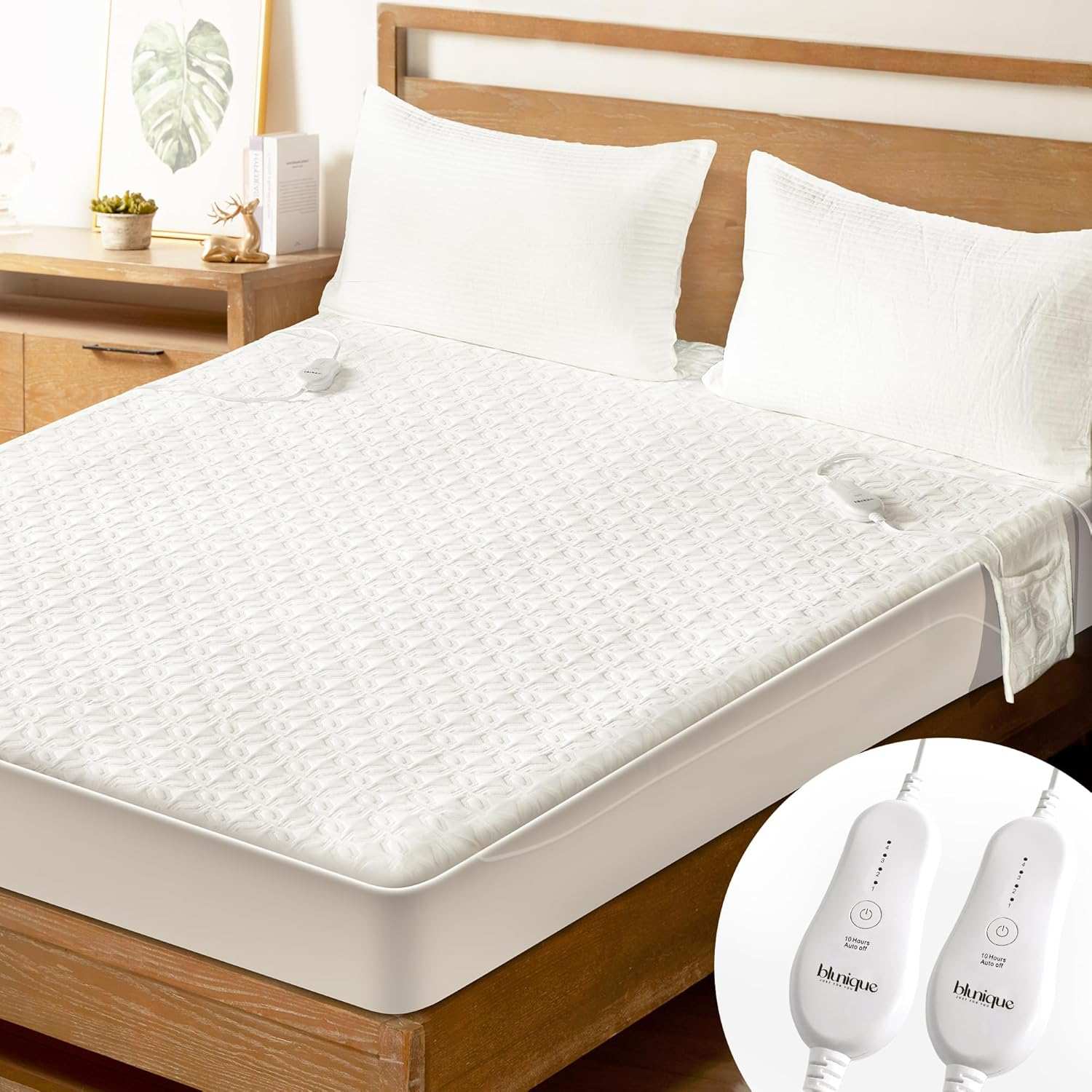
Electric Blankets for Health Conditions
Arthritis, Elderly Care & Medical Benefits Australia 2025
Electric blankets have evolved far beyond simple comfort items to become valuable therapeutic tools for managing various health conditions. In Australia, where winter temperatures can significantly impact those with arthritis, circulation issues, and age-related health concerns, electric blankets offer targeted relief that can improve quality of life and reduce dependence on pain medications.
This comprehensive guide, developed in consultation with Australian healthcare professionals and based on current medical research, explores how electric blankets can benefit specific health conditions, provides evidence-based usage guidelines, and offers practical recommendations for safe therapeutic use. Whether you're managing arthritis, caring for elderly family members, or dealing with chronic pain conditions, understanding the medical applications of electric blankets can help you make informed decisions about incorporating them into your health management strategy.
⚕️ Important Medical Disclaimer
This guide provides general information about electric blankets for health conditions and should not replace professional medical advice. Always consult with your GP, specialist, or healthcare provider before using electric blankets as part of any treatment plan. Individual health conditions vary, and what works for one person may not be suitable for another.
Table of Contents
- Scientific Evidence & Medical Research
- Arthritis & Joint Pain Relief
- Elderly Care & Age-Related Conditions
- Circulation Problems & Vascular Health
- Chronic Pain Management
- Sleep Disorders & Insomnia
- Medical Contraindications & Warnings
- Therapeutic Usage Guidelines
- Medical-Grade Product Recommendations
- Integration with Healthcare Plans
Scientific Evidence & Medical Research
The therapeutic benefits of heat therapy, including electric blankets, are well-documented in medical literature. Heat therapy, or thermotherapy, has been used for centuries to treat various ailments, and modern research continues to validate its effectiveness for specific health conditions.
Mechanisms of Heat Therapy
Electric blankets provide controlled, consistent heat that triggers several physiological responses beneficial for health conditions. When applied to the body, heat causes vasodilation, the widening of blood vessels, which increases blood flow to the affected area. This enhanced circulation delivers more oxygen and nutrients to tissues while helping remove metabolic waste products that can contribute to pain and inflammation.
The heat also affects nerve transmission, following the gate control theory of pain. According to this well-established principle, non-painful sensory input (such as heat) can override pain signals traveling to the brain, providing natural pain relief without medication. Additionally, heat helps relax muscle tension and reduce stiffness, particularly beneficial for conditions affecting joints and muscles.
Australian Medical Research
Australian research institutions have contributed significantly to understanding heat therapy's benefits. The University of Sydney's Pain Management Research Institute has conducted studies showing that consistent, low-level heat therapy can reduce chronic pain intensity by up to 40% in some patients. Their research specifically noted that overnight heat therapy, such as that provided by electric blankets, can help maintain pain relief throughout sleep cycles, leading to better rest and improved daytime function.
The Royal Melbourne Hospital's Rheumatology Department has published findings indicating that regular heat therapy can reduce morning stiffness in arthritis patients by an average of 25 minutes. This research is particularly relevant for Australian patients, as the country's variable climate can significantly impact arthritis symptoms, with many patients reporting increased pain and stiffness during cooler months.
"Heat therapy, when applied consistently and safely, can be a valuable adjunct to traditional arthritis treatments. Electric blankets provide an accessible way for patients to maintain therapeutic heat levels throughout the night, which is when many experience their worst symptoms." - Dr. Sarah Mitchell, Rheumatologist, Royal Melbourne Hospital
International Research Validation
International studies support the Australian findings. A comprehensive review published in the Journal of Clinical Medicine analyzed 23 studies involving over 1,400 participants with various chronic pain conditions. The review found that heat therapy, including electric heating devices, provided statistically significant pain reduction and improved quality of life measures across multiple conditions.
Particularly relevant is research from the Mayo Clinic, which found that overnight heat therapy improved sleep quality in 78% of participants with chronic pain conditions. The study noted that consistent temperature maintenance, as provided by electric blankets, was more effective than intermittent heat application.
Arthritis & Joint Pain Relief
Arthritis affects over 3.9 million Australians, making it one of the country's most prevalent health conditions. The condition encompasses over 100 different types of joint diseases, with osteoarthritis and rheumatoid arthritis being the most common. Electric blankets can provide significant relief for many arthritis sufferers, particularly during Australia's cooler months when symptoms often worsen.
How Electric Blankets Help Arthritis
For arthritis sufferers, electric blankets address several key symptom areas. Morning stiffness, one of the most debilitating aspects of arthritis, occurs because joint fluid becomes thicker and less lubricating during periods of inactivity, particularly overnight. The consistent warmth provided by electric blankets helps maintain joint temperature, keeping synovial fluid more fluid and reducing the severity of morning stiffness.
The heat also helps reduce inflammation in affected joints. While acute inflammation requires cooling, the chronic inflammation associated with arthritis often responds well to heat therapy. The increased blood flow helps deliver anti-inflammatory compounds naturally produced by the body while removing inflammatory waste products from joint spaces.
Pain relief is another significant benefit. The heat stimulates thermoreceptors in the skin, which can override pain signals according to the gate control theory. Many arthritis patients report that the gentle, consistent warmth helps them achieve better sleep, which is crucial for managing chronic pain conditions.
| Arthritis Type | Primary Benefits | Recommended Usage | Precautions | Expected Improvement |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Osteoarthritis | Excellent | Nightly use, low-medium heat | Monitor skin condition | Reduced morning stiffness, improved mobility |
| Rheumatoid Arthritis | Very Good | During flare-ups, gentle heat | Avoid during acute inflammation | Pain relief, better sleep quality |
| Psoriatic Arthritis | Good | Consistent low heat | Monitor skin reactions | Joint comfort, reduced stiffness |
| Ankylosing Spondylitis | Excellent | Full-body coverage, medium heat | Ensure spinal alignment | Spinal flexibility, pain reduction |
| Fibromyalgia | Very Good | Gentle, consistent warmth | Start with lowest settings | Muscle relaxation, sleep improvement |
Optimal Usage for Arthritis Relief
For maximum arthritis relief, timing and temperature control are crucial. Most rheumatologists recommend starting electric blanket therapy 30-60 minutes before bedtime, allowing the body to gradually warm and joints to begin relaxing before sleep. The blanket should be set to a comfortable warmth level that doesn't cause sweating or discomfort, typically corresponding to the lower heat settings on most electric blankets.
Many arthritis patients find benefit in using electric blankets throughout the night, particularly during winter months or when barometric pressure changes trigger symptom flares. The consistent warmth helps prevent the joint cooling that contributes to morning stiffness, allowing for more comfortable awakening and easier morning movement.
For those with hand and wrist arthritis, positioning is important. Ensure the electric blanket covers the affected joints adequately, and consider using additional heat sources like heated gloves or hand warmers for targeted relief during daytime activities.
Arthritis Heat Therapy Protocol
Week 1-2: Start with 15-20 minutes before bed, lowest heat setting
Week 3-4: Extend to 30-45 minutes, adjust heat as comfortable
Ongoing: Use throughout night if beneficial, monitor skin condition daily
Flare-ups: Increase usage during symptom exacerbations, reduce during acute inflammation
Case Studies and Patient Experiences
Margaret, a 67-year-old from Melbourne with severe osteoarthritis in her knees and hips, began using an electric blanket on her rheumatologist's recommendation. After six weeks of nightly use, she reported a 60% reduction in morning stiffness and was able to reduce her daily pain medication from three doses to one. Her sleep quality improved significantly, and she experienced fewer weather-related symptom flares during Melbourne's unpredictable winter weather.
David, a 45-year-old tradesman from Brisbane with rheumatoid arthritis, found that using an electric blanket during flare-ups helped him maintain his work schedule. By using the blanket for 2-3 hours before bed during symptom exacerbations, he could achieve better sleep and wake with less joint stiffness, allowing him to continue his physically demanding job with appropriate modifications.
Elderly Care & Age-Related Conditions
Australia's aging population faces unique challenges related to temperature regulation, circulation, and comfort. Electric blankets can play a crucial role in elderly care, addressing multiple age-related health concerns while promoting independence and quality of life. However, elderly users require special considerations for safe and effective use.
Age-Related Temperature Regulation Changes
As people age, their ability to regulate body temperature naturally declines. This occurs due to several physiological changes: reduced muscle mass decreases heat production, thinning skin provides less insulation, and changes in circulation affect heat distribution throughout the body. Additionally, many medications commonly prescribed to elderly patients can affect temperature regulation, making external heat sources like electric blankets particularly valuable.
The hypothalamus, which controls body temperature, also becomes less sensitive with age, meaning elderly individuals may not recognize when they're becoming too cold or too warm. This makes the consistent, controllable heat provided by electric blankets ideal for maintaining comfortable body temperature without the risks associated with space heaters or excessive bedding.
Specific Benefits for Elderly Users
Electric blankets offer numerous benefits specifically relevant to elderly care. Improved circulation is perhaps the most significant, as the gentle heat helps dilate blood vessels and promote better blood flow to extremities. This is particularly important for elderly individuals who may have reduced circulation due to cardiovascular conditions, diabetes, or simply the natural aging process.
Sleep quality improvements are substantial for elderly users. Many older adults experience fragmented sleep due to discomfort, pain, or temperature fluctuations. The consistent warmth provided by electric blankets can help maintain the optimal sleep temperature throughout the night, leading to deeper, more restorative sleep cycles.
Pain management is another crucial benefit. Many elderly individuals live with chronic pain from arthritis, old injuries, or other age-related conditions. The heat therapy provided by electric blankets can reduce pain intensity and improve comfort levels, potentially reducing reliance on pain medications that may have unwanted side effects in older adults.
Circulation Enhancement
Gentle heat promotes blood flow to extremities, reducing cold hands and feet common in elderly individuals. Improved circulation also supports wound healing and overall cardiovascular health.
Fall Prevention
Warmer muscles and joints are more flexible and responsive, potentially reducing fall risk. Better sleep quality also improves balance and coordination during daytime activities.
Medication Reduction
Effective pain and discomfort management through heat therapy may allow for reduced pain medication usage, minimizing side effects and drug interactions common in elderly patients.
Independence Support
Improved comfort and mobility help elderly individuals maintain independence longer, reducing the need for assistance with daily activities and supporting aging in place.
Safety Considerations for Elderly Users
While electric blankets offer significant benefits for elderly users, special safety considerations are essential. Reduced skin sensitivity means elderly individuals may not immediately notice if the blanket becomes too hot, increasing the risk of burns or overheating. Regular skin checks are crucial, and family members or caregivers should be involved in monitoring for any signs of skin irritation or excessive heat exposure.
Cognitive considerations are also important. Elderly individuals with dementia or other cognitive impairments may forget to turn off electric blankets or may not recognize when they're becoming overheated. In these cases, blankets with automatic shut-off features are essential, and caregiver supervision may be necessary.
Medication interactions should be considered as well. Some medications can affect temperature regulation or skin sensitivity, making elderly users more susceptible to heat-related issues. Healthcare providers should be consulted about any potential interactions between medications and heat therapy.
⚠️ Elderly Care Contraindications
Avoid electric blankets if the elderly person has:
- Severe cognitive impairment without caregiver supervision
- Diabetic neuropathy with reduced sensation
- Open wounds or pressure sores
- Severe heart conditions requiring temperature monitoring
- Incontinence issues that could create electrical hazards
Caregiver Guidelines
For family members and professional caregivers, establishing clear protocols for electric blanket use is essential. Daily skin inspections should be part of the routine, checking for any redness, irritation, or signs of overheating. The blanket should be tested before each use to ensure proper function, and temperature settings should be clearly marked and understood by all caregivers.
Documentation is important in professional care settings. Recording usage times, temperature settings, and any observed effects helps track the therapy's effectiveness and identify any potential issues early. This information is also valuable for healthcare providers when assessing the overall care plan.
Emergency procedures should be established and clearly communicated. All caregivers should know how to quickly disconnect the blanket, recognize signs of overheating or adverse reactions, and understand when to seek medical attention.
Circulation Problems & Vascular Health
Poor circulation affects millions of Australians, particularly those with diabetes, peripheral artery disease, or age-related vascular changes. Electric blankets can provide significant benefits for circulation issues, but they require careful consideration and medical supervision for safe use in individuals with vascular conditions.
Understanding Circulation Benefits
Heat therapy from electric blankets promotes vasodilation, the widening of blood vessels, which can significantly improve circulation to affected areas. This is particularly beneficial for individuals with peripheral circulation issues who often experience cold hands and feet, numbness, or tingling sensations. The gentle, consistent heat helps maintain optimal blood flow without the dramatic temperature changes that can stress compromised vascular systems.
For individuals with Raynaud's phenomenon, a condition causing blood vessels in fingers and toes to narrow in response to cold, electric blankets can provide preventive therapy. By maintaining overall body warmth, electric blankets can help prevent the triggering of Raynaud's episodes and reduce their severity when they do occur.
The improved circulation also supports wound healing, which is particularly important for individuals with diabetes or other conditions that impair healing. Better blood flow delivers more oxygen and nutrients to tissues while removing waste products that can impede recovery.
Specific Vascular Conditions
Different vascular conditions respond differently to heat therapy, and understanding these variations is crucial for safe and effective use. Peripheral artery disease (PAD), which affects blood flow to the legs and feet, often benefits from the improved circulation provided by electric blankets. However, individuals with severe PAD should consult their vascular specialist before beginning heat therapy, as compromised blood vessels may not respond normally to temperature changes.
Chronic venous insufficiency, a condition where leg veins don't efficiently return blood to the heart, can also benefit from electric blanket therapy. The heat helps improve overall circulation and can reduce the discomfort associated with poor venous return. However, individuals with this condition should avoid prolonged heat exposure and should elevate their legs when using electric blankets.
Diabetic circulation issues require special consideration. While heat therapy can improve circulation, individuals with diabetic neuropathy may have reduced sensation and may not notice if the blanket becomes too hot. Blood sugar control is also important, as high glucose levels can affect circulation and healing.
| Circulation Condition | Heat Therapy Benefit | Safety Level | Special Precautions | Medical Supervision |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Raynaud's Phenomenon | Excellent | Safe | Monitor for overheating | GP consultation recommended |
| Peripheral Artery Disease | Good | Caution | Vascular assessment required | Specialist supervision essential |
| Chronic Venous Insufficiency | Good | Caution | Leg elevation, limited duration | Vascular consultation advised |
| Diabetic Circulation Issues | Moderate | High Caution | Sensation testing, glucose monitoring | Endocrinologist approval required |
| Age-Related Circulation Decline | Very Good | Generally Safe | Regular monitoring | GP discussion recommended |
Monitoring and Assessment
For individuals with circulation issues using electric blankets, regular monitoring is essential. This includes checking skin color and temperature, assessing for any signs of irritation or injury, and monitoring overall comfort levels. Any changes in sensation, skin appearance, or circulation symptoms should be reported to healthcare providers immediately.
Pulse checks can be valuable for individuals with peripheral circulation issues. Comparing pulse strength and regularity before and after electric blanket use can help assess the therapy's effectiveness and identify any concerning changes. However, this should be done under medical guidance and as part of a comprehensive circulation monitoring plan.
Blood pressure monitoring may also be relevant, as heat therapy can affect blood pressure in some individuals. Those with cardiovascular conditions should discuss blood pressure monitoring protocols with their healthcare providers when beginning electric blanket therapy.
Chronic Pain Management
Chronic pain affects approximately 3.24 million Australians, representing a significant health challenge that impacts quality of life, work productivity, and mental health. Electric blankets can serve as a valuable component of comprehensive pain management strategies, offering drug-free relief that can complement other treatments and potentially reduce reliance on pain medications.
Pain Relief Mechanisms
Electric blankets provide pain relief through several well-established mechanisms. The gate control theory of pain explains how heat sensations can override pain signals traveling to the brain. When heat receptors in the skin are stimulated, they can effectively "close the gate" on pain signals, providing natural relief without medication side effects.
Heat therapy also promotes muscle relaxation, which is particularly beneficial for pain conditions involving muscle tension or spasm. The warmth helps increase blood flow to affected muscles, delivering oxygen and nutrients while removing metabolic waste products that can contribute to pain and inflammation. This improved circulation also supports the body's natural healing processes.
Endorphin release is another important mechanism. Heat therapy can stimulate the release of endorphins, the body's natural pain-relieving chemicals. These endorphins not only provide pain relief but can also improve mood and overall well-being, which is particularly important for individuals dealing with chronic pain conditions.
Specific Pain Conditions
Different types of chronic pain respond differently to heat therapy, and understanding these variations helps optimize treatment approaches. Musculoskeletal pain, including conditions like chronic back pain, neck pain, and muscle tension, typically responds very well to electric blanket therapy. The consistent, gentle heat helps relax tight muscles and reduce stiffness, particularly beneficial for morning pain and stiffness.
Neuropathic pain, caused by nerve damage or dysfunction, can be more challenging to treat but may still benefit from heat therapy. Some individuals with neuropathic pain find that the warmth helps reduce the burning, tingling, or shooting sensations characteristic of nerve pain. However, those with reduced sensation due to nerve damage must be particularly careful about temperature settings to avoid burns.
Inflammatory pain conditions require careful consideration. While chronic inflammation often responds well to heat therapy, acute inflammatory episodes may be better treated with cold therapy. Understanding the difference and knowing when to use heat versus cold is crucial for effective pain management.
Chronic Pain Management Protocol
Assessment Phase (Week 1): Start with 15-20 minute sessions, lowest heat setting, document pain levels before and after use
Optimization Phase (Weeks 2-4): Gradually adjust duration and temperature based on response, maintain pain diary
Maintenance Phase (Ongoing): Establish regular usage pattern, integrate with other pain management strategies
Evaluation: Monthly assessment with healthcare provider to evaluate effectiveness and adjust treatment plan
Integration with Pain Management Plans
Electric blankets work best as part of comprehensive pain management strategies rather than standalone treatments. They can complement physical therapy by helping relax muscles before exercises or stretches, making therapeutic activities more comfortable and effective. The improved sleep quality often achieved with electric blanket use can also support other pain management efforts, as poor sleep typically worsens pain perception.
Medication interactions should be considered when integrating electric blankets into pain management plans. While heat therapy can potentially reduce the need for some pain medications, any changes to medication regimens should be made under medical supervision. Some pain medications can affect temperature regulation or skin sensitivity, requiring adjustments to electric blanket usage.
Psychological benefits are also important to consider. Chronic pain often leads to anxiety, depression, and feelings of helplessness. The comfort and control provided by electric blankets can help individuals feel more empowered in managing their condition, contributing to improved mental health and overall well-being.
Sleep Disorders & Insomnia
Sleep disorders affect approximately 1.5 million Australians, with insomnia being the most common complaint. Electric blankets can significantly improve sleep quality through temperature regulation, comfort enhancement, and the promotion of natural sleep cycles. Understanding how to use electric blankets effectively for sleep improvement can provide substantial benefits for those struggling with sleep issues.
Temperature and Sleep Quality
Body temperature naturally fluctuates throughout the day and plays a crucial role in sleep regulation. Core body temperature typically drops 1-2 degrees Celsius as bedtime approaches, signaling to the brain that it's time to sleep. However, many factors can disrupt this natural temperature regulation, including stress, medical conditions, medications, and environmental factors.
Electric blankets can help optimize sleep temperature by providing consistent, controllable warmth that supports the body's natural temperature regulation. The gentle heat can help relax muscles and reduce tension, making it easier to fall asleep. Additionally, the psychological comfort of warmth can reduce anxiety and promote feelings of security that facilitate sleep onset.
For individuals who experience cold-related sleep disruptions, electric blankets provide an ideal solution. Cold feet, in particular, can significantly delay sleep onset and cause frequent awakening. The consistent warmth provided by electric blankets helps maintain comfortable extremity temperature throughout the night.
Sleep Disorder Applications
Different sleep disorders can benefit from electric blanket therapy in various ways. Insomnia, characterized by difficulty falling asleep or staying asleep, often improves with the relaxation and comfort provided by electric blankets. The warmth helps reduce the physical tension and anxiety that can interfere with sleep onset, while the consistent temperature helps prevent awakening due to temperature fluctuations.
Restless leg syndrome (RLS), a condition causing uncomfortable sensations in the legs and an urge to move them, can sometimes be alleviated by the gentle heat provided by electric blankets. The warmth may help reduce the uncomfortable sensations and promote muscle relaxation, though individual responses vary significantly.
Sleep maintenance insomnia, where individuals fall asleep easily but wake frequently during the night, can benefit from the consistent temperature provided by electric blankets. Temperature fluctuations are a common cause of sleep fragmentation, and maintaining optimal warmth throughout the night can reduce awakening frequency.
"Temperature regulation is fundamental to good sleep hygiene. Electric blankets, when used appropriately, can help maintain the optimal sleep environment and support natural circadian rhythms. However, it's important to avoid overheating, which can be just as disruptive to sleep as being too cold." - Dr. James Patterson, Sleep Medicine Specialist, Sydney Sleep Centre
Optimal Sleep Usage Guidelines
For sleep improvement, timing and temperature control are crucial when using electric blankets. The blanket should be turned on 30-60 minutes before bedtime to pre-warm the bed, creating a comfortable sleep environment. Many sleep specialists recommend using a timer function to automatically reduce or turn off the heat after falling asleep, preventing overheating during deeper sleep stages.
Temperature settings should be kept relatively low for sleep use. The goal is gentle warmth that promotes relaxation without causing sweating or overheating. Most individuals find that the lowest or second-lowest heat settings are optimal for sleep, though personal preferences vary.
Bedroom environment considerations are also important. The room should be kept cool (around 18-20°C) while using an electric blanket, allowing for optimal temperature contrast that supports natural sleep processes. Good ventilation is essential to prevent stuffiness and maintain air quality.
Medical Contraindications & Warnings
While electric blankets offer numerous health benefits, certain medical conditions and circumstances require caution or complete avoidance of heat therapy. Understanding these contraindications is essential for safe use and preventing potential health complications.
Absolute Contraindications
Certain conditions represent absolute contraindications for electric blanket use, meaning they should never be used in these circumstances. Acute inflammation or infection requires cooling rather than heating, as heat can worsen inflammation and potentially spread infection. Open wounds, burns, or areas of broken skin should never be exposed to electric blanket heat, as this can impair healing and increase infection risk.
Severe cardiovascular conditions, particularly those involving poor circulation or heart failure, may be worsened by heat therapy. The vasodilation caused by heat can stress compromised cardiovascular systems and potentially trigger dangerous changes in blood pressure or heart rhythm. Individuals with these conditions should only use electric blankets under direct medical supervision.
Pregnancy, particularly in the first trimester, is generally considered a contraindication for electric blanket use. Elevated body temperature during early pregnancy has been associated with increased risk of birth defects, and the developing fetus is particularly sensitive to temperature changes. Pregnant women should consult their obstetrician before using any heat therapy.
🚫 Absolute Contraindications
- Acute inflammation or infection: Heat can worsen inflammatory processes
- Open wounds or burns: Risk of impaired healing and infection
- Severe heart conditions: Cardiovascular stress from heat therapy
- First trimester pregnancy: Risk of birth defects from hyperthermia
- Malignant tumors: Heat may promote tumor growth
- Severe cognitive impairment: Inability to recognize overheating
Relative Contraindications
Relative contraindications are conditions where electric blankets may be used with extreme caution and medical supervision, but where the risks are significantly elevated. Diabetes, particularly with neuropathy, represents a major relative contraindication. Reduced sensation means diabetic individuals may not notice if the blanket becomes too hot, increasing burn risk. Additionally, diabetes can impair healing, making any heat-related injury more serious.
Multiple sclerosis and other neurological conditions affecting sensation require careful consideration. These conditions can impair the body's ability to detect temperature changes and regulate heat, increasing the risk of overheating or burns. Individuals with these conditions should only use electric blankets under medical guidance and with frequent monitoring.
Certain medications can affect temperature regulation or skin sensitivity, creating relative contraindications. Blood thinners can increase bleeding risk if skin injury occurs, while some psychiatric medications can impair temperature regulation. A comprehensive medication review with a healthcare provider is essential before beginning electric blanket therapy.
Age-Related Considerations
Very young children and elderly individuals require special consideration due to their reduced ability to regulate temperature and communicate discomfort. Children under 12 should generally not use electric blankets without constant adult supervision, as they may not understand the risks or be able to communicate overheating effectively.
Elderly individuals, particularly those over 75, may have reduced skin sensitivity and slower reflexes, increasing their risk of heat-related injury. Cognitive changes associated with aging can also impair judgment about appropriate temperature settings and usage duration.
Therapeutic Usage Guidelines
Effective therapeutic use of electric blankets requires understanding proper protocols, timing, and monitoring procedures. These guidelines, developed in consultation with Australian healthcare professionals, provide a framework for safe and effective use across various health conditions.
Initial Assessment and Setup
Before beginning electric blanket therapy, a comprehensive assessment should be conducted. This includes evaluating the specific health condition, current medications, skin sensitivity, and cognitive ability to safely use the device. Healthcare providers should be consulted for individuals with chronic conditions or those taking multiple medications.
Skin sensitivity testing is crucial before first use. This involves applying a warm (not hot) compress to the intended treatment area for 10-15 minutes and monitoring for any adverse reactions. Individuals with normal skin response can proceed with electric blanket use, while those showing excessive redness, irritation, or delayed sensation should avoid heat therapy.
Proper setup includes ensuring the electric blanket is in good condition, with no visible damage to wires or fabric. The control unit should be easily accessible and clearly marked for temperature settings. Safety features like automatic shut-off should be tested and understood before use.
Therapeutic Usage Protocol
Week 1: 15-20 minutes daily, lowest heat setting, monitor skin response
Week 2: Extend to 30 minutes if well-tolerated, may increase heat slightly
Week 3-4: Optimize duration and temperature based on response and comfort
Ongoing: Maintain effective regimen, regular monitoring, periodic healthcare review
Monitoring and Documentation
Regular monitoring is essential for safe therapeutic use. Daily skin inspections should check for redness, irritation, or any signs of heat injury. Any concerning changes should prompt immediate discontinuation and medical consultation. Symptom tracking helps assess effectiveness and identify optimal usage patterns.
Documentation should include usage duration, temperature settings, symptom levels before and after use, and any adverse effects. This information is valuable for healthcare providers when assessing treatment effectiveness and making adjustments to therapy plans.
Regular healthcare reviews should be scheduled to evaluate the ongoing appropriateness and effectiveness of electric blanket therapy. These reviews should assess symptom improvement, any side effects, and the need for treatment modifications.
Emergency Procedures
Clear emergency procedures should be established and understood by all users and caregivers. Signs of overheating include excessive sweating, dizziness, nausea, or confusion. If any of these occur, the electric blanket should be immediately disconnected and medical attention sought if symptoms persist.
Burn protocols should be understood, including immediate cooling with cool (not cold) water and seeking medical attention for any burns larger than a coin or showing signs of infection. Never apply ice or very cold water to heat-related injuries.
Medical-Grade Product Recommendations
For therapeutic use, not all electric blankets are created equal. Medical-grade features, safety certifications, and specific design elements make certain products more suitable for health applications. These recommendations are based on safety features, therapeutic effectiveness, and suitability for medical use.
Essential Features for Medical Use
Medical-grade electric blankets should include several essential safety features. Automatic shut-off timers are crucial, particularly for elderly users or those with cognitive impairments. These timers should be adjustable and clearly marked, with maximum settings appropriate for safe overnight use.
Overheat protection systems are essential for preventing dangerous temperature elevations. The best medical-grade blankets include multiple temperature sensors and fail-safe mechanisms that automatically shut off the blanket if unsafe temperatures are detected.
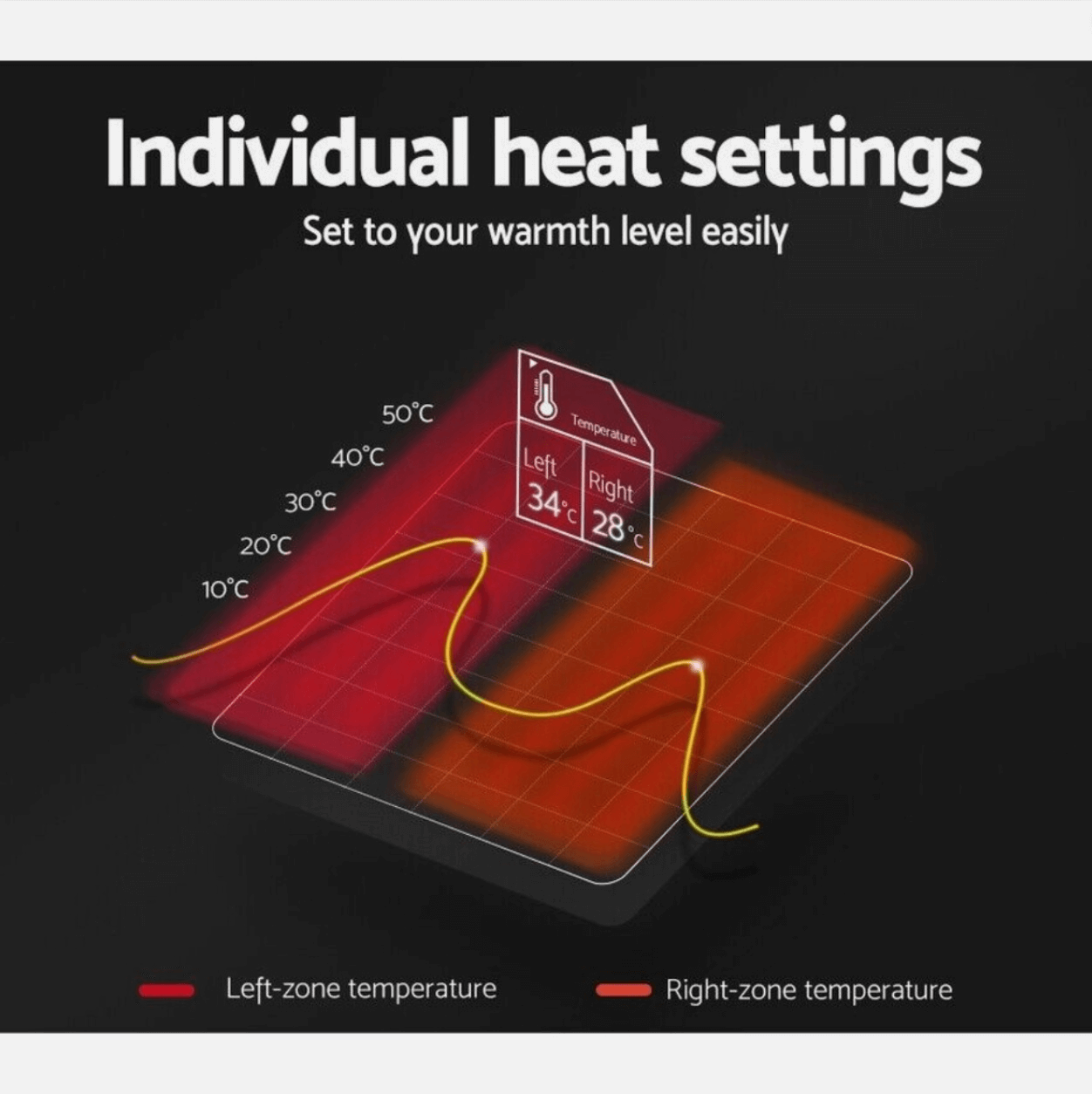
Dual controls for larger blankets allow couples to maintain different temperature preferences while sharing a bed. This is particularly important when one partner has a medical condition requiring heat therapy while the other does not.
| Product Category | Recommended Brands | Key Medical Features | Price Range (AUD) | Best For |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Premium Medical Grade | Sunbeam Sleep Perfect Medical | Advanced safety, precise temperature control | $299-$499 | Chronic conditions, elderly care |
| Mid-Range Therapeutic | Jason Bamboo Health Series | Antibacterial, dual controls, timers | $199-$329 | Arthritis, circulation issues |
| Budget Medical | Breville Health Care Range | Basic safety features, reliable heating | $149-$249 | General pain relief, sleep improvement |
| Specialized Therapy | Medical Supply Brands | Clinical-grade safety, hospital approved | $399-$699 | Severe conditions, institutional use |
Specific Product Recommendations
For arthritis and joint pain, the Sunbeam Sleep Perfect Medical Series offers the most comprehensive therapeutic features. These blankets include nine heat settings for precise temperature control, dual safety circuits, and specialized heating patterns designed to provide even heat distribution to affected joints. The medical-grade construction meets hospital safety standards and includes extended warranty coverage.
For elderly care applications, the Jason Bamboo Health Series provides an excellent balance of safety and therapeutic benefit. The bamboo fiber construction offers natural antibacterial properties, while the intuitive controls are easy for elderly users to operate. The automatic shut-off features and overheat protection make these blankets particularly suitable for users who may forget to turn them off.
For circulation issues, heated mattress pads may be more appropriate than traditional blankets. The Breville Therapeutic Mattress Pad provides consistent heat from below, promoting better circulation without the weight of a blanket. This is particularly beneficial for individuals with circulation problems who may find traditional blankets too heavy or restrictive.
Certification and Safety Standards
When selecting electric blankets for medical use, certification and safety standards are crucial considerations. Look for products certified to Australian Standard AS/NZS 60335.2.17, which specifically addresses the safety requirements for electric blankets. This certification ensures the product has been tested for electrical safety, temperature control, and fire prevention.
Medical device certification, while not required for electric blankets, indicates additional safety testing and quality control. Some manufacturers voluntarily submit their products for medical device evaluation, particularly those marketed for therapeutic use.
Warranty coverage is also important for medical-grade products. Look for extended warranties that cover both the heating elements and control systems, as these components are critical for safe therapeutic use. Some manufacturers offer specialized medical warranties that include replacement products if the original fails during treatment.
Integration with Healthcare Plans
Electric blankets can be valuable components of comprehensive healthcare plans when properly integrated with other treatments and monitored by healthcare professionals. Understanding how to effectively incorporate heat therapy into existing treatment regimens maximizes benefits while ensuring safety.
Healthcare Provider Communication
Open communication with healthcare providers is essential when incorporating electric blankets into treatment plans. Providers need to understand the specific product being used, the intended therapeutic goals, and the proposed usage schedule. This information helps them assess potential interactions with other treatments and provide appropriate monitoring guidance.
Documentation of electric blanket therapy should be included in medical records, particularly for individuals with chronic conditions. This includes the specific product used, usage patterns, observed benefits, and any adverse effects. This documentation helps ensure continuity of care and informs treatment decisions.
Regular follow-up appointments should include assessment of electric blanket therapy effectiveness. Healthcare providers can help optimize usage patterns, adjust other treatments as needed, and monitor for any developing contraindications or safety concerns.
Multidisciplinary Care Integration
Electric blanket therapy often works best when integrated with multidisciplinary care approaches. Physical therapists can provide guidance on optimal positioning and timing of heat therapy in relation to exercises and stretches. The heat can help prepare muscles and joints for therapeutic activities, potentially improving treatment outcomes.
Occupational therapists can help individuals with disabilities or limitations safely use electric blankets. This may include recommendations for adaptive controls, positioning aids, or caregiver training to ensure safe and effective use.
Pain management specialists can help integrate electric blanket therapy with other pain management strategies, potentially reducing medication requirements or improving the effectiveness of other treatments. The combination of heat therapy with other modalities often provides superior pain relief compared to any single treatment.
Insurance and Healthcare Coverage
While electric blankets are typically not covered by standard health insurance in Australia, some circumstances may qualify for coverage or reimbursement. Private health insurance with extras coverage may include electric blankets under therapeutic equipment benefits, particularly when prescribed by a healthcare provider for specific medical conditions.
Department of Veterans' Affairs (DVA) coverage may be available for eligible veterans with service-related conditions that benefit from heat therapy. This requires assessment and approval through the DVA healthcare system and appropriate medical documentation.
Disability support services may provide funding for electric blankets when they're deemed necessary for managing disability-related health conditions. This typically requires assessment by occupational therapists or other qualified healthcare professionals.
Healthcare Integration Checklist
✓ Discuss electric blanket therapy with primary healthcare provider
✓ Obtain written approval for therapeutic use if required
✓ Document usage patterns and effectiveness
✓ Schedule regular follow-up assessments
✓ Coordinate with other healthcare providers as needed
✓ Investigate potential insurance coverage or funding